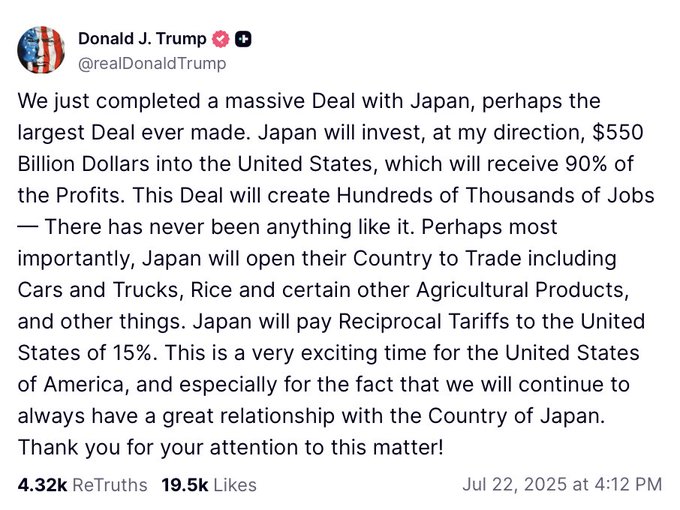
The japan trade deal signed on 22 July 2025 is headline news across the United States and Asia, reshaping conversations about japan, tariffs, and equity markets. This landmark us japan trade deal—often called the “largest trade deal in history” by President Trump—sets a lower 15 percent reciprocal tariff on Japanese exports, secures a promised $550 billion Japanese investment into the United States, and immediately lifted toyota stock along with the Nikkei 225. Below is an easy-to-read guide that explains the japan trade deal details, its back-story, and why analysts are already debating the long-term impact in a fresh wave of japan trade deal analysis.

Key Facts of the Japan Trade Deal July 2025
The new agreement rewrites the rules that would have imposed a 25 percent tariff on Japanese goods from 1 August. Instead, a standardized rate of 15 percent is now applicable, while Japan commits to allowing more American competition in sensitive sectors, including cars, trucks, rice, and specialty agricultural items.

| Deal Element | Before 22 Jul 2025 | After Japan Trade Deal | Significance |
| Standard rate applied to all products from Japan | 10% since April 2 (“Liberation Day” tariffs) | 10% unchanged | Maintains original baseline |
| Additional tariff threatened for failure to reach agreement | 15% add-on from 1 Aug (total 25%) | Cancelled | Avoids steep cost spike |
| Autos & parts special tariff | 25% (30% threat letter) | 15% unified | Big win for Japanese carmakers |
| Japanese investment commitment | None | $550 bn over five years | Targets U.S. infrastructure & energy |
| U.S. market openings in Japan | Limited quotas in 2019 mini-deal | Wider access for cars, rice, LNG | Benefits Midwest farmers & Texas LNG |
The immediate market reaction was dramatic: the Nikkei 225 closed up 3.5 percent, Toyota Motor Corporation ADRs leapt 14.3 percent, and U.S. S&P futures increased by 0.8 percent as traders processed the implications of the lower-tariff approach.
Why This Japan Trade Deal Happened Now
Both governments faced hard deadlines. Trump’s 25 percent “reciprocal tariff” threat was set to bite on 1 August, while Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba was reeling from a double-chamber election setback on 20 July. Rapid progress on a high-profile economic accord provides political capital on both sides of the Pacific. Analysts note three deeper drivers:
- Trump wants quick tariff wins to bolster the “America First” platform ahead of the 2026 mid-terms.
- Japan seeks certainty for car exports (28 percent of its 2024 shipments to the U.S.) and a hedge against China-centric supply chains.
- Both nations have already cooperated on critical minerals (the March 2023 U.S.–Japan Critical Minerals Agreement) and see this broader pact as a logical next step.
How Toyota Stock and Other Japanese Shares Reacted
| Company | Ticker (Tokyo) | Close 22 Jul 2025 | % Change | Reason |
| Toyota Motor | 7203.T | ¥2 854 | +14.34% | A reduction in the tariff from 25% to 15% enhances the earnings forecast. |
| Honda Motor | 7267.T | ¥1 650 | +11.15% | Similar export relief, gains from U.S. EV plant spend |
| Nissan Motor | 7201.T | ¥329 | +8.28% | Lower tariff avoids 32% worst-case scenario |
| Subaru Corp | 7270.T | ¥2 249 | +18.6% | U.S.-centric sales model highly sensitive to tariff cut |
| Nikkei 225 | — | 41 171.32 | +3.51% | Broad risk-on rally after deal news |
Wall Street’s reaction mirrored Tokyo: pre-market gains in Toyota’s NY-listed ADR (TM) echoed the Japanese move, while futures tied to the Dow added over 200 points in early Wednesday trading.
Sector Impact Highlights
- Automotive: 15 percent tariff simplifies supply-chain calculations; Japanese firms may accelerate U.S. EV assembly to offset any remaining duties.
- Agriculture: American rice and beef exporters gain tariff-free quotas, ending a long dispute over Japan’s high import mark-ups.
- Energy: A joint U.S.–Japan LNG project in Alaska—rumoured at $44 billion—heads the investment slate, supporting Gulf Coast gas-export infrastructure.
- Technology & Minerals: The 2023 critical-minerals pact dovetails with this deal to secure lithium, nickel, and cobalt flows for EV batteries and semiconductors.
Japan Trade Deal Analysis: Winners and Questions
Economists widely label the pact a relief rally rather than a full free-trade agreement. The uniform 15 percent duty still adds cost compared with the pre-Trump era but removes the cliff edge risk for manufacturers. Analysts at Nomura calculate that Toyota’s effective tariff burden drops from a worst-case 32 percent to an average 13.5 percent under blended sourcing rules, lifting FY-2026 net profit projections by ¥290 billion ($1.98 billion).
Others worry about implementation gaps. No full text has been published; critics argue that investment pledges lack enforcement triggers and could rely on re-labelled capital already earmarked for U.S. plants. Furthermore, high 50 percent steel and aluminium duties remain, leaving Japan’s metalmakers exposed.
Macro Outlook Table
| Metric | Pre-Deal Forecast 2025 | Post-Deal Revision | Source |
| U.S.–Japan goods trade deficit (US$ bn) | –$100 bn | –$92 bn | Treasury Mid-Session Review |
| U.S. auto import price index | +5.8% YoY | +3.2% YoY | Bureau of Labor Statistics projection |
| Japan GDP growth 2025 | 1.2% | 1.5% | Bank of Japan update |
| Nikkei 225 year-end target | 40 000 | 42 500 | Goldman Sachs research |
Timeline of Key US-Japan Trade Moments 2019–2025
| Date | Milestone |
| Oct 2019 | Limited U.S.–Japan Trade Agreement enters force (agriculture & digital). |
| Mar 2023 | Critical Minerals Agreement signed; qualifies Japanese-sourced battery materials for U.S. EV tax credits. |
| Apr 2 2025 | Trump announces 10% baseline “Liberation Day” tariffs plus threatened 15% add-on (total 25%). |
| Jul 1 2025 | Trump letter warns of 30% auto tariff from 1 Aug absent a deal. |
| Jul 22 2025 | “Massive” US-Japan trade deal signed; 15% reciprocal tariff, $550 bn investment pledge. |
| Aug 1 2025 | Previous tariff deadline cancelled; 15% rate takes effect. |
How the Deal Affects Everyday Consumers
- American car shoppers may see modest price drops on Japan-built models if automakers pass through tariff savings.
- U.S. rice growers get expanded access to Japan’s premium consumer market, a boost for Arkansas and California.
- Japanese pension funds investing in U.S. Treasuries could channel part of the $550 billion commitment, potentially capping long-term U.S. borrowing costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q 1 What is included in the japan trade deal with us?
The agreement sets a flat 15 percent tariff on Japanese goods—lower than the threatened 25 percent—while Japan commits to $550 billion of U.S. Investment and broader opportunities for American automobiles, rice, and liquefied natural gas.
Q 2 How did toyota stock react?
Toyota’s Tokyo-listed shares spiked 14.3 percent after the announcement, reflecting relief over the lower tariff and renewed growth prospects.
Q 3 Does the deal remove all tariffs?
No. The baseline 10 percent Liberation Day tariff remains, and metals like steel and aluminium stay at 50 percent. The 15 percent rate replaces the threatened higher layer.
Q 4 Is this japan trade deal trump’s first pact with Tokyo?
No. A narrower 2019 mini-deal cut some farm tariffs. The 2025 accord is broader, covering autos, agriculture, and investment.
Q 5 What are the next steps for congress?
Because the deal was announced via executive authority, formal congressional ratification is not currently required, though lawmakers may hold oversight hearings on transparency and enforcement.
Q 6 Will U.S. EV tax credits change?
EV credits tied to critical minerals remain under the 2023 Critical Minerals Agreement, which treats Japan as a qualifying partner for lithium, nickel, and cobalt sourcing.
Q 7 Could the tariff rate be reduced further?
Trade officials hinted at a review clause for 2027; a shift toward EV-only tariff lines or a complete phase-out could be negotiated depending on compliance.
Q 8 How big is $550 billion in context?
It equals roughly 10 percent of Japan’s 2024 GDP and exceeds the cumulative Japanese FDI stock in the U.S. since 1980. Analysts expect phased disbursements into infrastructure, energy, and high-tech manufacturing.
Read more article please click on the Link.



